特性在框架中的应用也是很普遍,只需要在相应的类、字段、属性、函数等上面加上这个特殊的小东西就会在相应的元素上面添加一些特殊的应用效果,下面就为大家简单的介绍下特性的原理和应用场景
在往期的博客中有介绍过一些特性
- Unity Debug输出到屏幕并保存到本地中的Conditional("EnableLog")特性
- Unity Attributes中Unity自带的特性
- Obsolete、Serializable等
下面咱们来聊一聊特性到底是个什么,都能干什么?为什么说它是一个灵活的小工具。但是在了解特性之前需要对反射有点小基础,不熟悉的小伙伴可以看下Unity C#基础之 反射反射,程序员的快乐
万事具备咱们就进入特性的小世界~~~
完整示例工程下载
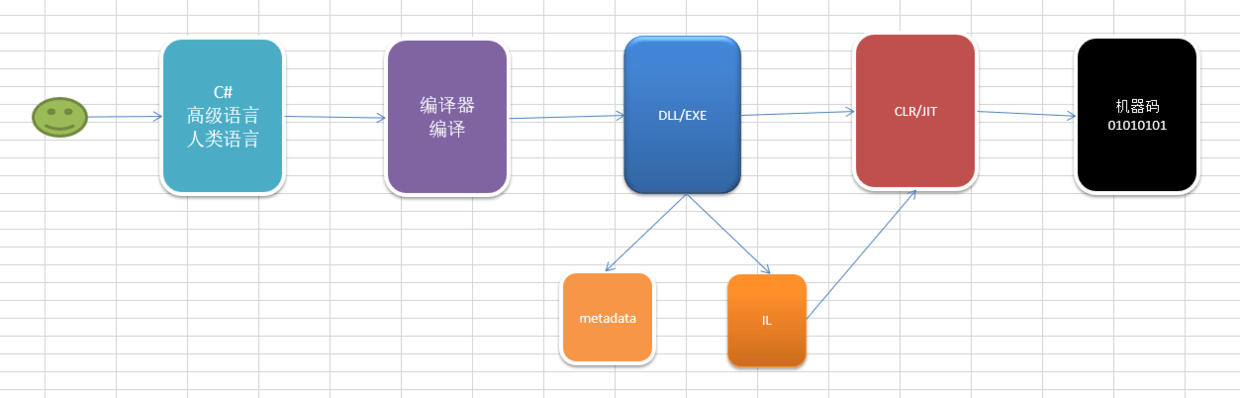
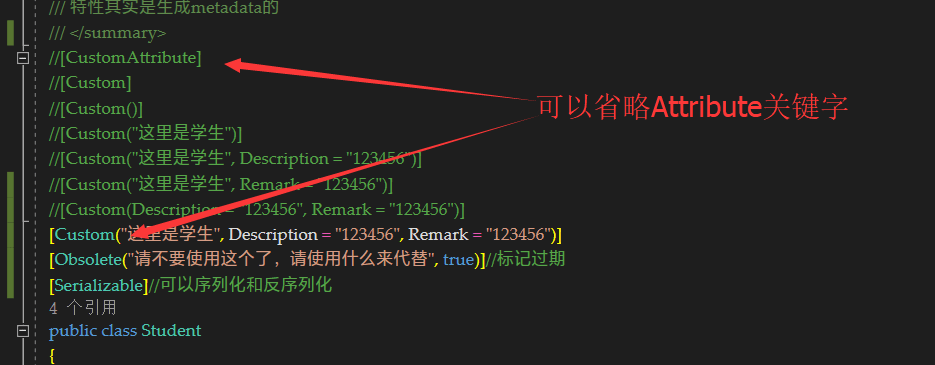
特性:是一个类,可以用来标记元素,编译时生成到metadata里,平时不影响程序的运行,除非主动用反射去查找,可以得到一些额外的信息/操作,然后给提供了更丰富扩展空间 。特性可以在不破坏类型封装的前提下,额外的增加功能 例如AOP:面向切面编程 。特性是一个直接/间接继承自Attribute的类,约定俗成用attribute结尾,然后声明的时候可以省略
按照 《特性是一个直接/间接继承自Attribute的类,约定俗成用attribute结尾,然后声明的时候可以省略》的说法,我们先自定义一个特性
using System;
namespace MyAttribute
{
/// <summary>
/// AttributeTargets.All(说明这个特性可以标记在什么元素上,类、字段、属性、方法、返回值等元素,ALL代表所有)
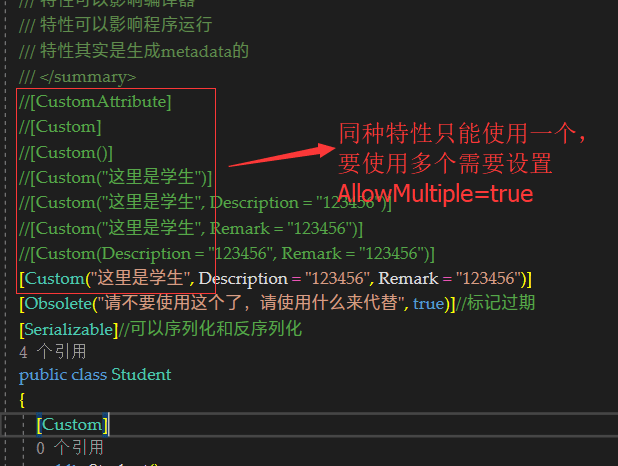
/// AllowMultiple(说明这个特性在同一个元素上使用的次数,默认一个元素只能标记一种特性,但可以多种特性并存)
/// Inherited(说明这个特性是否可以继承)
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.All, AllowMultiple = false, Inherited = true)]
public class CustomAttribute : Attribute
{
public CustomAttribute()
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是CustomAttribute");
}
public CustomAttribute(string remark)
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是CustomAttribute带参数");
}
public string Remark { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public void Show()
{
Console.WriteLine($"This is {this.GetType().Name}");
}
}
public class CustomChildAttribut : CustomAttribute
{
}
public class AuthorityAttribute : Attribute
{
public string Remark { get; set; }
public bool IsLogin()
{
return new Random().Next(100, 200) > new Random().Next(99, 199);
}
}
}
这样我们一个自定义的特性就建立好了,然后我们怎么使用的呢?看下面的事例
先创建一个student类然后我们可以这么添加
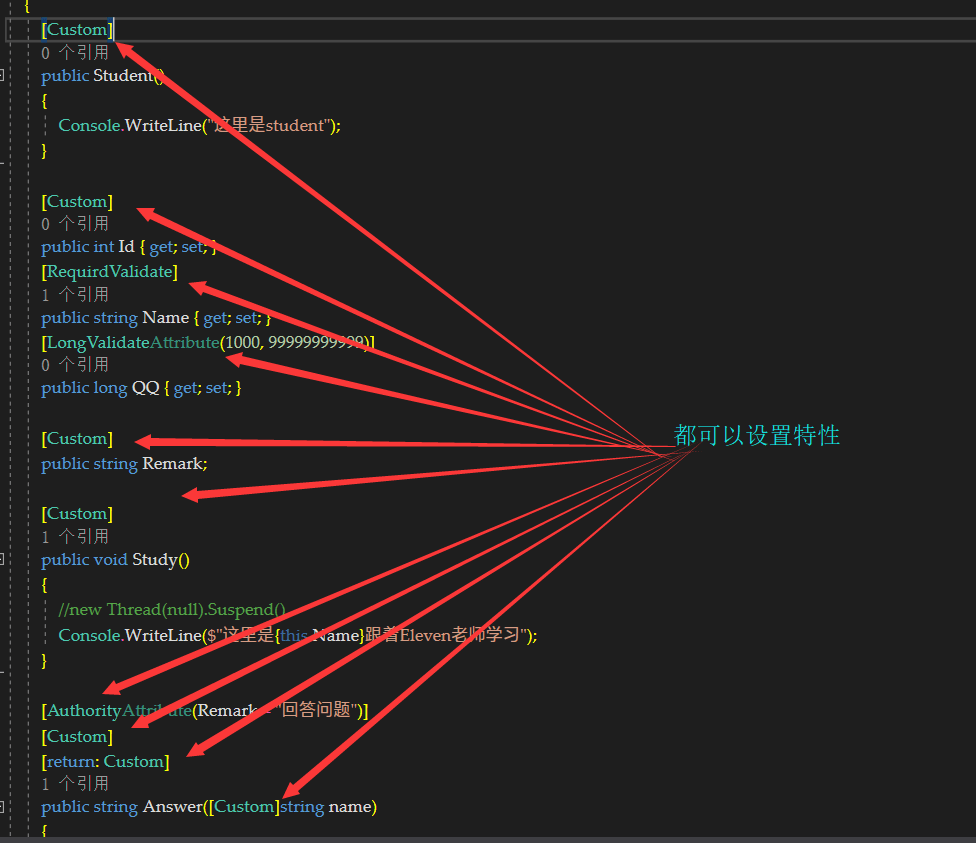
using MyAttribute.Extend;
using System;
namespace MyAttribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 这里是注释,除了让人看懂这里写的是什么,
/// 对运行没有任何影响
///
/// 特性可以影响编译器
/// 特性可以影响程序运行
/// 特性其实是生成metadata的
/// </summary>
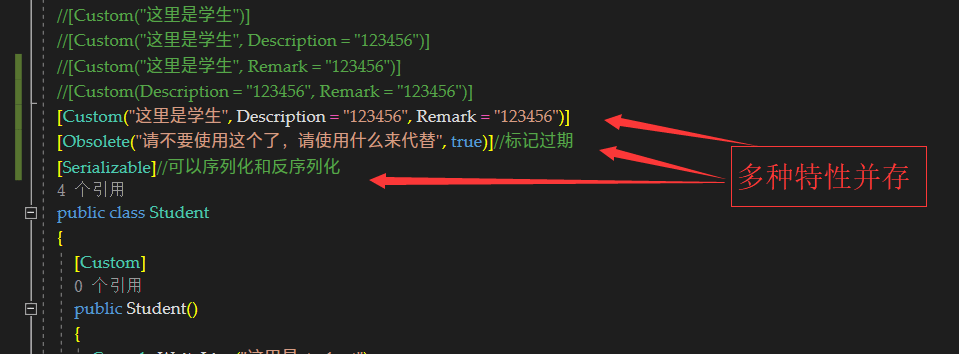
//[CustomAttribute]
//[Custom]
//[Custom()]
//[Custom("这里是学生")]
//[Custom("这里是学生", Description = "123456")]
//[Custom("这里是学生", Remark = "123456")]
//[Custom(Description = "123456", Remark = "123456")]
[Custom("这里是学生", Description = "123456", Remark = "123456")]
//[Obsolete("请不要使用这个了,请使用什么来代替", true)]//标记过期
//[Serializable]//可以序列化和反序列化
public class Student
{
[Custom]
public Student()
{
Console.WriteLine("这里是student");
}
[Custom]
public int Id { get; set; }
[RequirdValidate]
public string Name { get; set; }
[LongValidateAttribute(1000, 99999999999)]
public long QQ { get; set; }
[Custom]
public string Remark;
[Custom]
public void Study()
{
//new Thread(null).Suspend()
Console.WriteLine($"这里是{this.Name}跟着Eleven老师学习");
}
[AuthorityAttribute(Remark = "回答问题")]
[Custom]
[return: Custom]
public string Answer([Custom]string name)
{
return $"This is {name}";
}
}
}
这样我们自定义的特性和特性可以使用的地方就都清楚了,但是我们怎么让这个特殊的类(特性)发挥用处呢?那就要看下面的事例
在刚刚的student类中我们在很多元素上标记了特性,下面我要让这些特性发挥作用
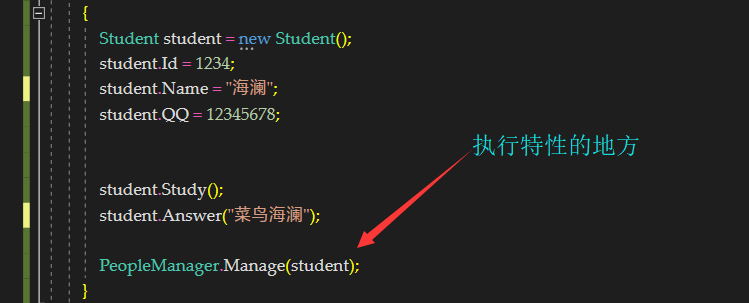
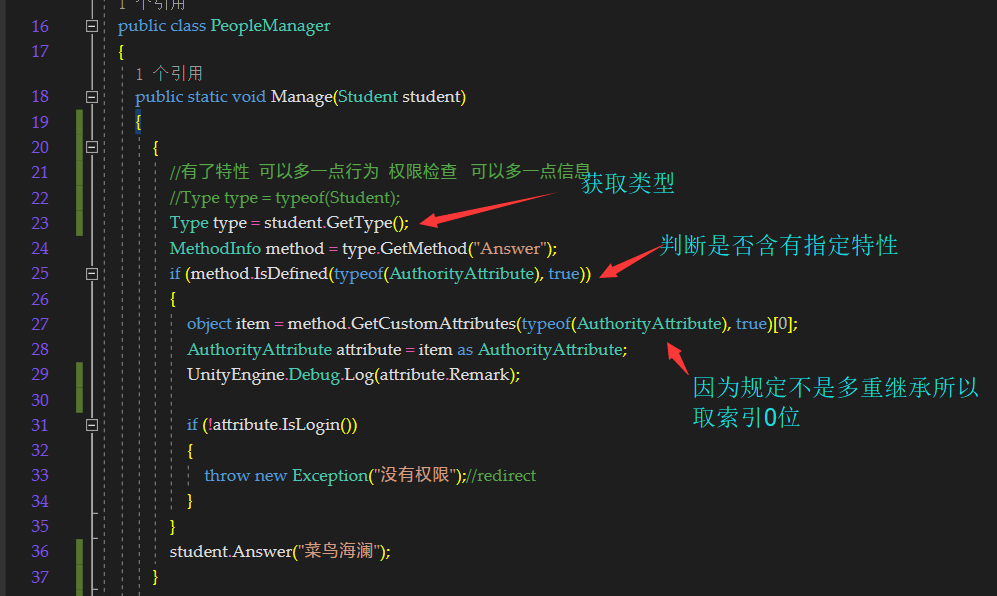
PeopleManager全部code,包括对类、属性、字段、构造函数、方法、方法参数、方法返回值的特性检测
using MyAttribute.Extend;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 特性 编译后是 metadata 只有反射才能使用
/// 包了一层 专门来使用特性
/// </summary>
public class PeopleManager
{
public static void Manage(Student student)
{
{
//有了特性 可以多一点行为 权限检查 可以多一点信息
//Type type = typeof(Student);
Type type = student.GetType();
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Answer");
if (method.IsDefined(typeof(AuthorityAttribute), true))
{
object item = method.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AuthorityAttribute), true)[0];
AuthorityAttribute attribute = item as AuthorityAttribute;
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(attribute.Remark);
if (!attribute.IsLogin())
{
throw new Exception("没有权限");//redirect
}
}
student.Answer("菜鸟海澜");
}
#region
{
Type type = student.GetType();
if (type.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))//检测这个类是否含有指定的特性
{
object item = type.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(CustomAttribute), true)[0];
{
CustomAttribute attribute = item as CustomAttribute;
attribute.Show();
}
}
foreach (var item in type.GetProperties())//检测属性是否含有指定的特性
{
if (item.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
object oAttribute = item.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(CustomAttribute), true)[0];
CustomAttribute attribute = oAttribute as CustomAttribute;
// Do Something....
}
}
foreach (var item in type.GetFields())//检测字段是否含有指定的特性
{
if (item.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
object oAttribute = item.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(CustomAttribute), true)[0];
CustomAttribute attribute = oAttribute as CustomAttribute;
// Do Something....
}
}
foreach (var item in type.GetConstructors())//检测构造函数是否含有指定的特性
{
if (item.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
object oAttribute = item.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(CustomAttribute), true)[0];
CustomAttribute attribute = oAttribute as CustomAttribute;
// Do Something....
}
}
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Answer");
if (method.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))//检测对应的方法是否含有指定的特性
{
object oAttribute = method.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(CustomAttribute), true)[0];
CustomAttribute attribute = oAttribute as CustomAttribute;
// Do Something....
}
foreach (var item in method.GetParameters())//检测对应函数的参数是否含有指定的特性
{
if (item.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
object oAttribute = item.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(CustomAttribute), true)[0];
CustomAttribute attribute = oAttribute as CustomAttribute;
// Do Something....
}
}
if (method.ReturnParameter.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))//检测对应函数的返回值是否含有指定的特性
{
object oAttribute = method.ReturnParameter.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(CustomAttribute), true)[0];
CustomAttribute attribute = oAttribute as CustomAttribute;
// Do Something....
}
}
#endregion
}
}
}
特性扩展

完成code
using System;
namespace MyAttribute.Extend
{
public abstract class AbstractValidateAttribute : Attribute
{
public abstract bool Validate(object oValue);
}
public class LongValidateAttribute : AbstractValidateAttribute
{
private long _lMin = 0;
private long _lMax = 0;
public LongValidateAttribute(long lMin, long lMax)
{
this._lMin = lMin;
this._lMax = lMax;
}
public override bool Validate(object oValue)
{
return this._lMin < (long)oValue && (long)oValue < this._lMax;
}
}
public class RequirdValidateAttribute : AbstractValidateAttribute
{
public override bool Validate(object oValue)
{
return oValue != null;
}
}
public class DataValidate
{
public static bool Validate<T>(T t)
{
Type type = t.GetType();
bool result = true;
foreach (var prop in type.GetProperties())
{
if (prop.IsDefined(typeof(AbstractValidateAttribute), true))
{
object item = prop.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AbstractValidateAttribute), true)[0];
AbstractValidateAttribute attribute = item as AbstractValidateAttribute;
if (!attribute.Validate(prop.GetValue(t)))
{
result = false;
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace MyAttribute.Extend
{
/// <summary>
/// 是给枚举用 提供一个额外信息
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Enum | AttributeTargets.Field)]
public class RemarkAttribute : Attribute
{
public RemarkAttribute(string remark)
{
this.Remark = remark;
}
public string Remark { get; private set; }
}
public static class RemarkExtend
{
/// <summary>
/// 扩展方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="enumValue"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static string GetRemark(this Enum enumValue)
{
Type type = enumValue.GetType();
FieldInfo field = type.GetField(enumValue.ToString());
if (field.IsDefined(typeof(RemarkAttribute), true))
{
RemarkAttribute remarkAttribute = (RemarkAttribute)field.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(RemarkAttribute));
return remarkAttribute.Remark;
}
else
{
return enumValue.ToString();
}
}
}
[Remark("用户状态")]
public enum UserState
{
/// <summary>
/// 正常
/// </summary>
[Remark("正常")]
Normal = 0,
/// <summary>
/// 冻结
/// </summary>
[Remark("冻结")]
Frozen = 1,
/// <summary>
/// 删除
/// </summary>
[Remark("删除")]
Deleted = 2
}
}
牛,一般U3d定制按钮或者header就是这么回事。